What is EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) & How It Works
EDI, or Electronic Data Interchange, is a technology that helps trading partners and organizations get more done, speed up logistics timelines and eliminate manual errors by automating business-to-business (B2B) communications. EDI helps many organizations that produce, ship, purchase and sell goods or provide care, from retailers and manufacturers to logistics firms, airlines, healthcare providers, insurers and more.
Though it's been in use since the 1960s, EDI is finding new use today, enabling supply chain automation, digital transformation and even as a key part of workflow and business process automation. In this rundown, we give you a solid understanding of EDI and quickly introduce you to all the basics of EDI, including:
- What is EDI?
- EDI Use Cases
- EDI Benefits
- Common EDI Challenges
- How EDI Works
- EDI Documents
- EDI Implementation
This page also serves as an EDI resource hub, with links to more resources on EDI types, standards, transactions and integration - everything you need to know about EDI, all in one convenient place.
What is EDI?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the automated, computer-to-computer exchange of standard electronic business documents between business partners over a secure, standardized connection.
Let's break down this EDI definition, piece by piece, to give you a full sense of what EDI is and means.
Computer-to-Computer EDI
- EDI replaces manual B2B communications, such as postal mail, fax and email.
- Documents flow directly from the sender's computer application (e.g. a logistics system) to the receiver's computer application (e.g., an order management system).
Traditional Manual Process

Automated EDI Process
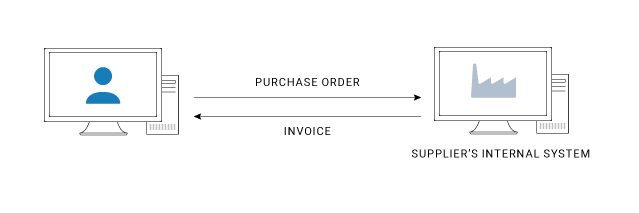
Business Documents
- 1000s of standard business transaction documents can be sent automatically using EDI.
- Some common examples include: purchase orders, invoices, shipping statuses, customs information, inventory documents and payment confirmations.
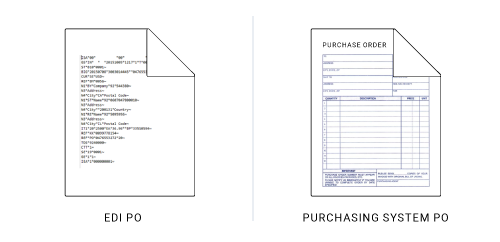
Standard EDI Format
- EDI documents are processed by computers and use standard, computer-friendly formats.
- Standards describe each piece of data and its format (e.g., type of document, parties involved, actions to take, mmddyy).
- Standards eliminate company-to-company variations, allowing each business partner's computer system to speak a common language.
- There are a variety of EDI standards for various industries, regions and use cases - each with different versions, so EDI partners must use the same standard and version
- Popular standards include: ANSI X12 in the U.S., UN/EDIFACT globally and industry-specific standards, such as HIPAA

Business Partners
- The exchange of EDI documents is typically between two different organizations, referred to as business partners or trading partners.
- Example: Company A may buy goods from Company B. Company A sends Purchase Orders to Company B, which sends Invoices and Shipment Notices to Company A.
Secure, Standardized Connection
- EDI uses a range of secure protocols to facilitate the secure exchange of EDI documents.
- Partners must use the same, agreed-upon protocol to exchange EDI files or work with an intermediary who can facilitate exchanges if the partners use different protocols.
- Some protocols require more EDI technology infrastructure than others, but EDI software, such as CData Arc, now facilitates exchanges with minimal investment.
- The protocols range from long-established technologies, such as FTP, to web-based EDI via AS2, API-based systems, such as AS4, and other options, such as mobile EDI.
EDI Automation
- EDI messages can be sent automatically using pre-configured workflows.
- Businesses typically use EDI translators - either as software or via an EDI service provider - to translate EDI documents for use in internal applications, enabling automated processing.
- Processes can be extended to work with data integration and workflows within an organization.
- Example: once a company receives an EDI Purchase Order, the logistics system generates a task for warehouse staff to move goods from inventory to shipping.
EDI vs. Traditional Paper or Email Communications
To illustrate the meaning of EDI, or electronic data interchange, let's compare how a typical purchasing transaction would go between two trading partners using traditional paper or email communications vs. using EDI.
Traditional methods:
- The buyer either receives a notification in his system to place an order, or, after querying the inventory, determines he needs to place an order.
- The buyer enters data onto the screen of a purchasing system to create the PO, prints and mails it or emails it to the vendor.
- The vendor receives the PO, either days later or via email (along with a long list of other communications) and manually enters it into the sales order system.
- The vendor prints an invoice and encloses it with the shipment and/or sends it separately by mail or email.
- The buyer manually enters the invoice into the accounts payable system.
In this example, a paper system can add a week of back-and-forth shipping time to the process. Both email and paper are susceptible to manual data entry errors, lengthening order time.
EDI process:
- The buyer's procurement system, which uses EDI, auto-generates and sends an EDI-formatted PO when inventory reaches a pre-specified level.
- In minutes the vendor's sales order system, using EDI software, receives the EDI PO.
- The supplier's system automatically notifies their shipping department to send goods.
- Once the goods are packed and ready to ship, the shipping system generates an Advanced Ship Notices (ASN) to send to the buyer's receiving department
- The vendor's ERP system then generates an EDI invoice to transmit to the buyer's accounts payable system
The entire EDI process can be completed in an hour.
What Is EDI Used For? 5 Real-World Use Cases
No definition of EDI is complete without real-world applicability. Electronic Data Interchange is useful for a wide variety of functions spanning many thousands of specific information exchanges. Here are just some of the most common scenarios where EDI is helpful, from among the many thousands of transaction types EDI handles every day.
EDI in Supply Chain (Retail, Manufacturing, Automotive)
- Purchasing
- Order fulfillment
- Shipping confirmations
- International orders
- Parts order fulfillments
EDI in Healthcare
- Exchanging patient health information
- Health insurance processing
- Prescription information exchanges
EDI in Logistics
- Scheduling shipments
- Tracking goods
EDI in Accounting
- Generating invoices
- Providing audit trails
EDI in Aviation
- Flight information exchanges
- Passenger name records (PNRs)
- International compliance and standardization
6 Benefits of EDI for Businesses
EDI helps businesses improve supply chain speed, accuracy, efficiency and costs, and some of the greatest EDI benefits come at the strategic business level. Here, we cover what EDI means, practically, for business.
Faster Processing
- EDI can speed up business cycles by 61 percent
- EDI enables transactions in minutes instead of days or weeks spent on postal mail or back-and-forth email communications
- Automating paper-based tasks frees up your staff for higher-value tasks and provides them the tools to be more productive
- Quick processing of accurate business documents leads to fewer re-worked orders, stock outs and cancellations
- Automating application data exchange across a supply chain ensures critical data is sent on time and tracked in real time
- Shortening order processing and delivery helps organizations reduce inventory
Lower Costs
- EDI reduces the transaction costs of paper, printing, reproduction, storage, filing, postage and document retrieval, saving businesses more than 35 percent on transaction costs
- For buyers that handle numerous transactions, using EDI can also result in millions of dollars of annual savings due to early payment discounts
- In some cases, EDI is just 1/20th the cost of manual order processing, slashing costs by a factor of 20
- EDI also eliminates costly errors due to illegible faxes, lost orders or incorrectly taken phone orders
More Accuracy, Fewer Errors
- EDI reduces error transactions by 30-40 percent
- EDI eliminates human errors from illegible handwriting, lost mail and keying errors
Better Relationships
- Sellers benefit from improved cash flow and reduced order-to-cash cycles
- In fact, EDI can reduce the order-to-cash cycle time by more than 20%, improving business partner transactions and relationships
- Reducing errors also saves partners valuable time and frustration handling data disputes
Strategic Benefits
- EDI provides real-time visibility into transaction status, enabling faster decision-making and better responsiveness to customer and market demands, helping businesses adopt a demand-driven approach
- Product enhancements and delivery enjoy shorter lead times
- Streamlines the process of entering new territories, as EDI provides a common worldwide business language
Environmental Benefits
- EDI promotes sustainability and reduces CO2 emissions by replacing paper-based processes with electronic alternatives
- EDI increases operational efficiencies, leading to fewer errors and less energy waste
3 Common EDI Challenges
Document preparation
The structure of EDI documents differs from other common data standards like CSV files, database tables, and JSON objects. Converting your existing data into a valid EDI document can pose a technical challenge for organizations just getting started with EDI.
When you need to send critical business data to your partner, the process of building an EDI document out of the data within your systems requires specific training or expertise within your team. Usually, organizations rely on dedicated EDI integration tools to help prepare outbound EDI documents to ensure validity.
EDI document translation
Similar to the need for preparing outbound documents, handling inbound documents can pose a technical challenge for businesses just getting started with EDI. After receiving an EDI document, you frequently need to extract the information contained in the document and integrate this information into other systems within your organization.
Translating the EDI document standard into XML, JSON, or other more workable formats can be a laborious process without the appropriate tools that streamline the EDI process.
Connect & transmit EDI documents
Whenever critical business data is exchanged, the need for security and reliability is high. Thankfully, many standards and protocols exist that have already solved the common challenges of encryption, verification, and non-repudiation.
However, implementing any one of these protocols can be a steep technical task. Platforms that perform the work of implementing these protocols on your organization's behalf can help speed up onboarding time and smooth partner relationships.
How EDI Works
There are three steps in the process of sending EDI documents: prepare the documents, translate them into an EDI format and transmit them to a partner.
One common process automated with EDI is the exchange of purchase orders (POs) and invoices. To give you a good example of how EDI works, we'll illustrate the EDI process for POs and invoices.
1. Document Preparation
Following the example of a PO and invoice, this is where a buyer prepares an order in a purchasing system.
- The buyer collects and organizes the data so it will work with EDI
- For example, instead of printing a PO, the system creates an electronic file with the necessary information to build an EDI document
So how would you properly prepare documents? There are several approaches, including:
- Exporting computer-based data from spreadsheets or databases
- Reformatted electronic reports into data files
- Enhancing apps to create output files ready for EDI standard translation
- Purchasing EDI software that can turn documents from your systems into EDI files
- Human data entry
Ideally, you would want your system to eliminate as much human data entry as possible to save time and improve accuracy.
2: EDI Document Translation
The next step is to feed your document through EDI translation software to convert your internal data format into the EDI standard format using the appropriate segments and data elements. Alternatively, you can send your data to an EDI service provider, who handles translation to and from the EDI format on your behalf.
In our example, the PO is translated into an EDI 850 purchase order document.
3: Connect & Transmit EDI Documents
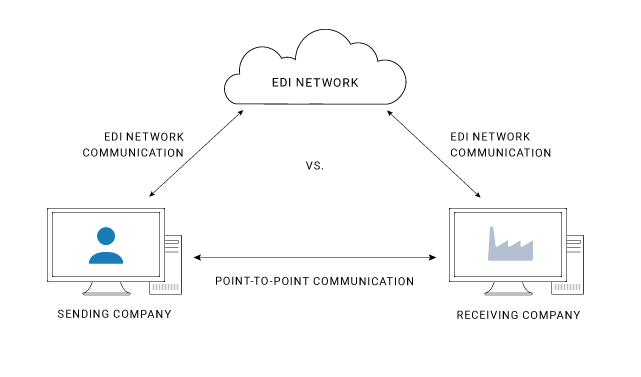
Once the PO is translated to the EDI 850 purchase order format, it's ready for transmission to the supplier. There are several ways to connect to a partner via EDI. The most common of include:
- Direct, point-to-point EDI connection via a secure Internet protocol, such as AS2
- Connect to an EDI network provider, also referred to as a Value Added Network (VAN) provider
- A combination of both Direct EDI and VAN, depending on the partners involved and the transaction volume
In the case of an EDI network provider, or value-added network (VAN), the buyer uses their preferred communications protocol, ensuring reliable, secure EDI transmission. Then, the network provider connects to the supplier using the supplier's preferred communications protocol, ensuring the supplier receives the order. VANs can reduce setup and maintenance in some cases but tend to be more expensive than point-to-point integration for many use cases, as they charge a fee for each transaction or even line item.
Data security and control are maintained throughout the transmission process using passwords, user identification and encryption. Both the buyer and vendor EDI applications automatically edit and check documents for accuracy.
In our full guide to the types of EDI protocols, we unpack the various EDI file transfer options and the technologies they use to help you select the right protocol(s) for your organization.
The Key Components of an EDI Transaction
To give you a better view of what EDI is, let's look at the key parts of what goes into EDI. An EDI document is comprised of three core pieces: envelopes, segments and data elements, formatted to follow a specific EDI standard.
EDI documents, such as an 850 purchase order, must adhere to strict formatting rules that define exactly where and how each piece of data in the document goes so the EDI translator on the receiving computer can instantly find all key data, such as the buyer's company name, PO number, items purchased and price. Then, the data will be fed into the supplier's order entry system in the proper internal format without requiring any manual entry.
EDI Envelopes for Transmission
EDI document transmission uses a system of three envelopes to house transaction sets:
- Message envelope
- Group envelope
- Interchange envelope
Segments
A segment in an EDI transaction set is a group of like data elements.
Data Elements
The data elements in an EDI transaction set are the individual data in the document, such as the item being purchased, quantity of items purchased, etc.
How to Achieve EDI Compliance
Achieving EDI compliance ultimately means three things:
- Setting up your EDI infrastructure
- Aligning your EDI setup with your trading partners' EDI systems
- Certifiably adhering to common standards
EDI Infrastructure
To get started with EDI, you'll need to either procure, set up or outsource the following key components:
- EDI software for communications, mail boxing of EDI transactions, EDI mapping and EDI translation
- Internet communications, VAN, etc. as required by various partners
- Hardware: a server or PC, communication devices and peripherals
- Secured office space and monitored security
- Data backups and redundant power for reliability
- Software for any integration of EDI transactions with back office systems
- Maps for each EDI document type exchanged with each partner to map EDI records into useable business documents
In addition, you'll need to train your team in how to use your EDI software and communication devices or select an EDI integration partner to set it all up and train your team.
Aligning with Your Partners
Your EDI is only as valuable as your integrations with your partners' systems. Big keys include:
- Determining which EDI protocols you'll use to send and receive EDI documents (e.g. AS2, SFTP, etc.) - See our guide to the types of EDI protocols
- Selecting and implementing exchanges for the correct EDI documents, or transactions (e.g. 850 purchase orders) - See our exhaustive EDI transactions library
- Nailing down the use cases when you'd send and receive each EDI document
- Tying EDI into your other operational, logistics or 3PL, accounting and order fulfillment systems - you may want solutions that help with broader process implementations
- Properly integrating EDI mapping, translation and testing with your partners
Depending on your setup, this can include mutually selecting EDI solutions and EDI integration providers. Ultimately, you'll need the right solutions to help you maximize your partnership. The simpler the setup (with the most versatile tools), the faster you can implement EDI and start saving time & money while growing relationships with your partner.
Certification to Common Standards
Common, certified standards are the glue that holds EDI together. Key certifying bodies govern these standards and can help you evaluate various solutions.
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) - certifies the X12 EDI standard used in the U.S.
- UN/CEFACT - certifies the popular international EDIFACT standard
- GS1 - certifies several industry-specific international EDI standards (built on EDIFACT)
- Drummond - certifies EDI software through rigorous interoperability testing, ensuring that different EDI tools can successfully communicate with each other
Integration Guide
If you're starting out on an integration project, we highly recommend checking out our EDI integration guide. It will help you get up and running with EDI through a structured approach.
B2B EDI Integration with CData Arc
CData Arc is the All-in-One EDI Solution for B2B EDI integration. It provides EDI translation, transmission and mapping, with powerful data integrations to plug EDI directly into your processes. We also work with an extensive network of EDI integration partners who can assist you in implementation. And we offer world-class support, with both cloud SaaS and on-premise options.
CData Arc
All-in-One EDI Solution
- EDI: Complete Guide
- What is EDI?
- EDI Use Cases
- EDI Benefits
- Common EDI Challenges
- How EDI Works
- EDI Documents
- EDI Implementation







